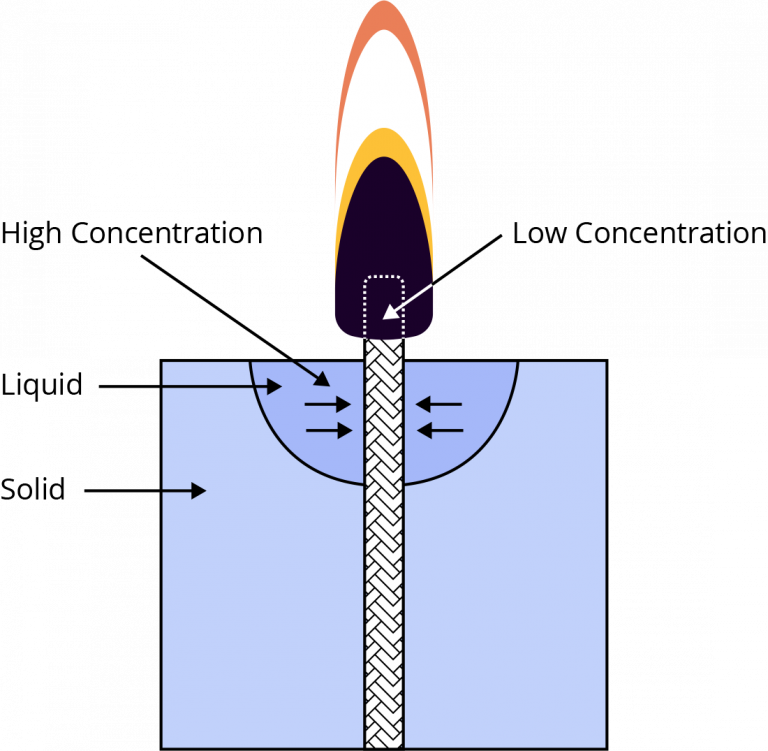
Diffusion:
Liquid wax diffuses into the wick saturating the cotton fibers.
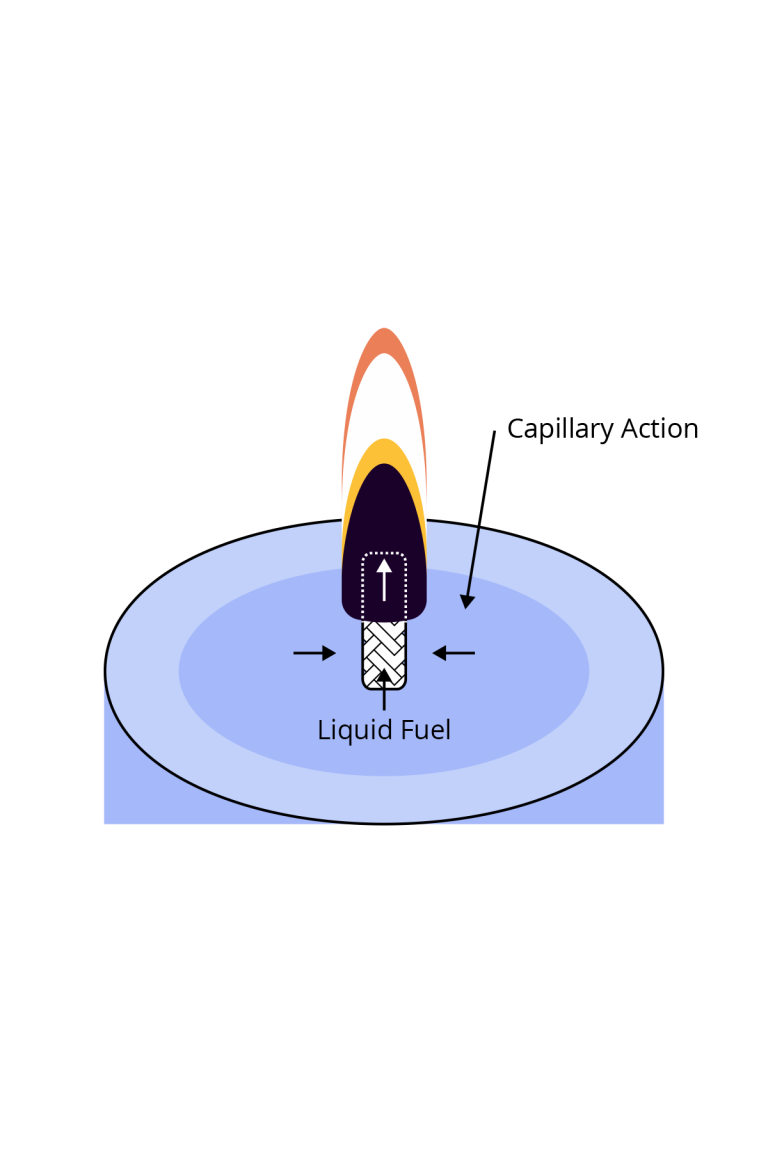
Capillary Action:
The fuel moves up the wick as it is consumed through the process of capillary action.
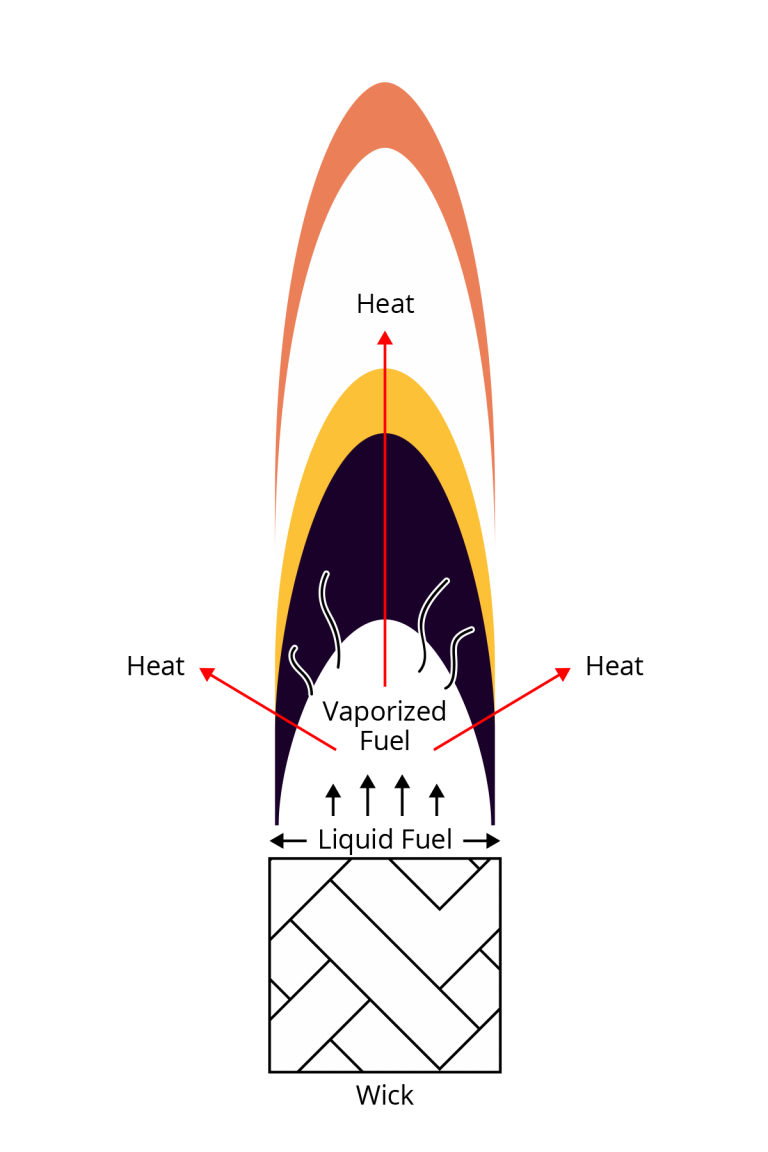
Vaporization of Fuel:
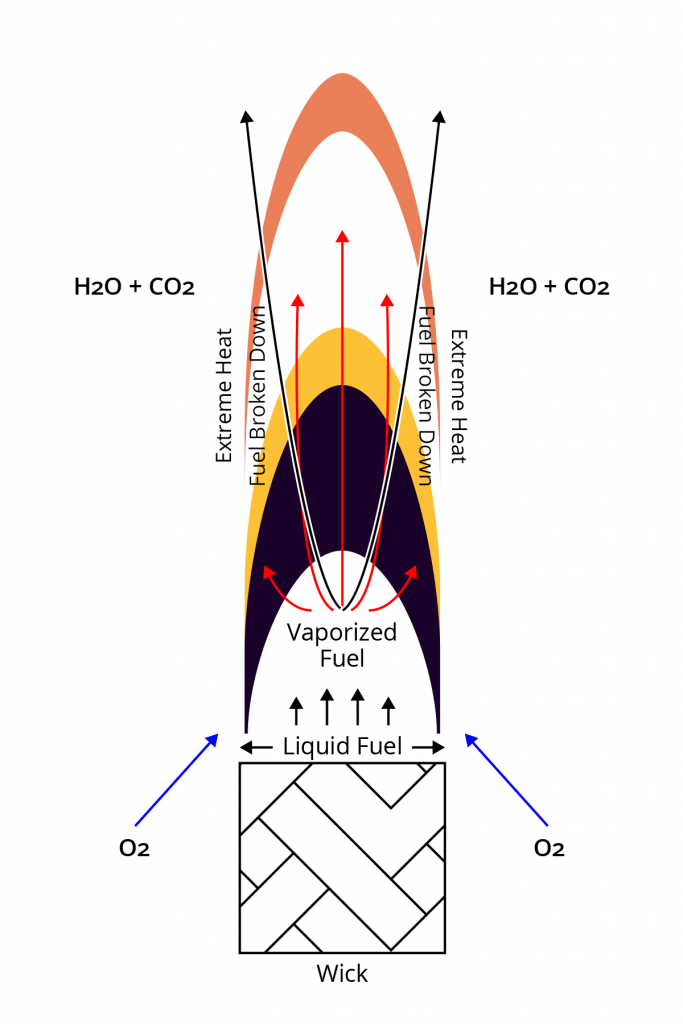
The flame’s heat vaporizes the liquid fuel to begin the combustion process.
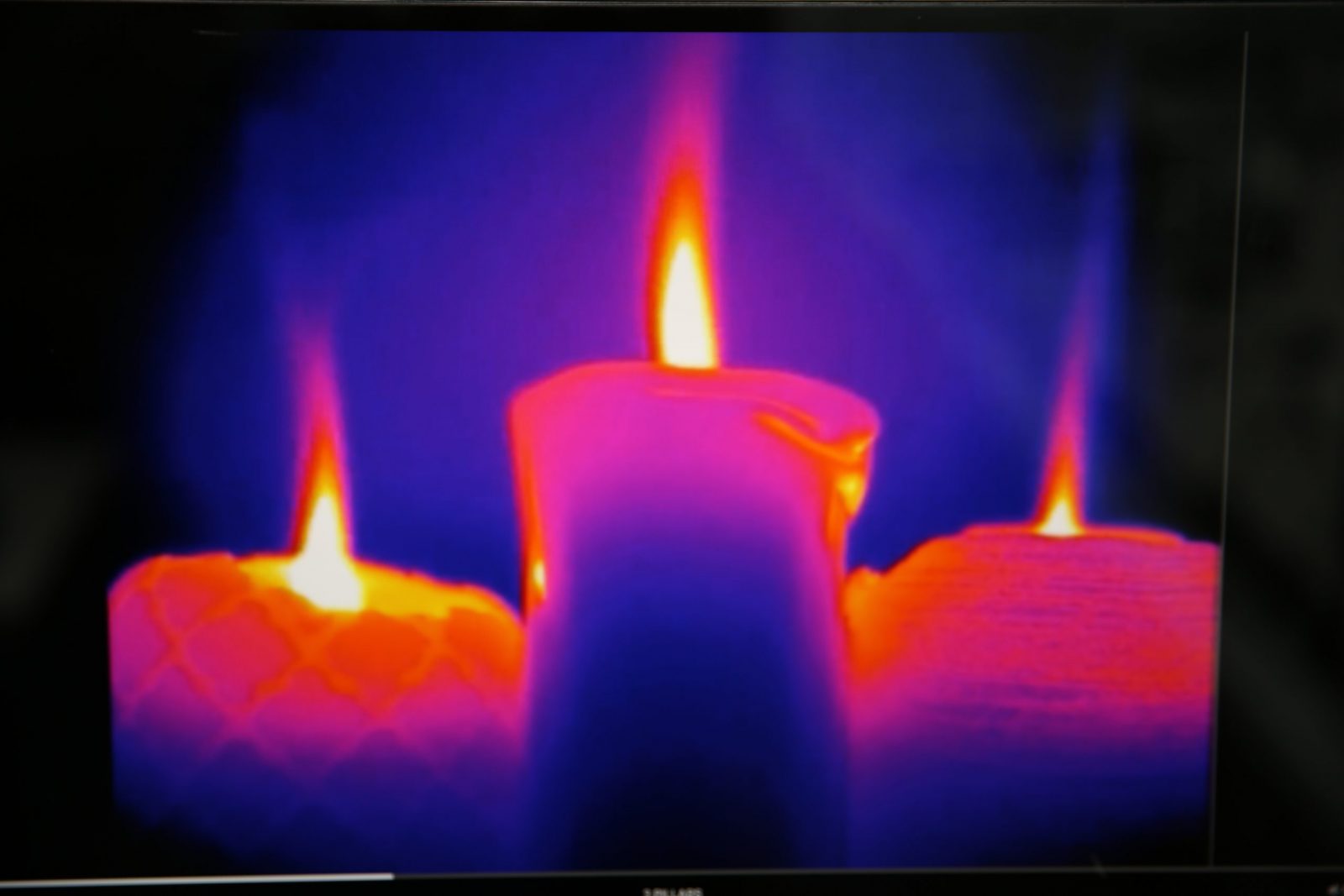
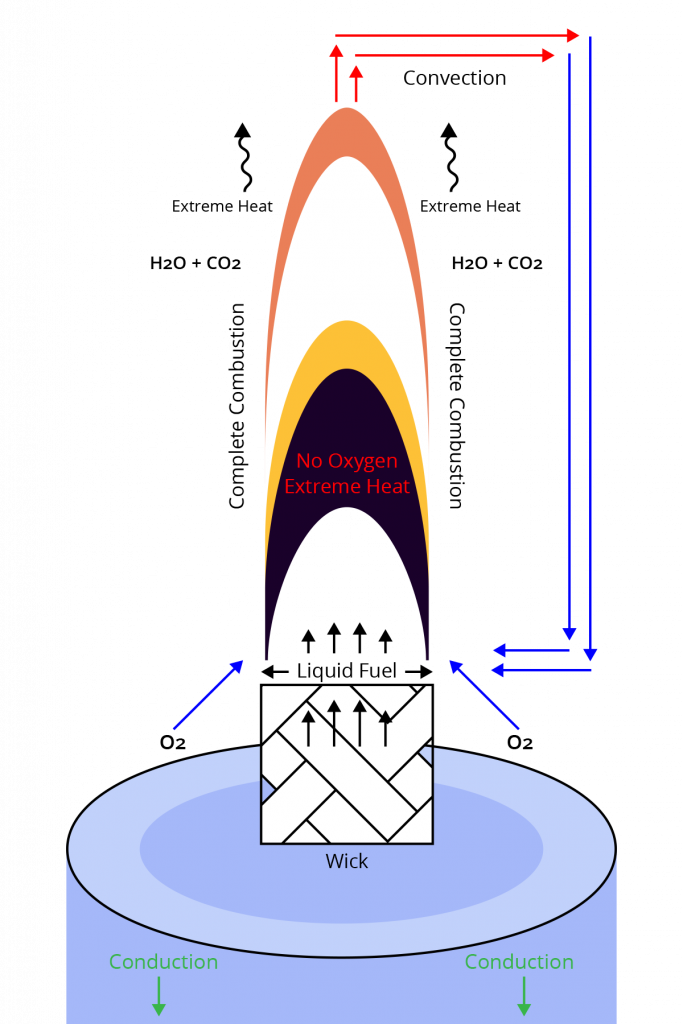
Incomplete Combustion:
All candle flames have varying degrees of complete and incomplete combustion.
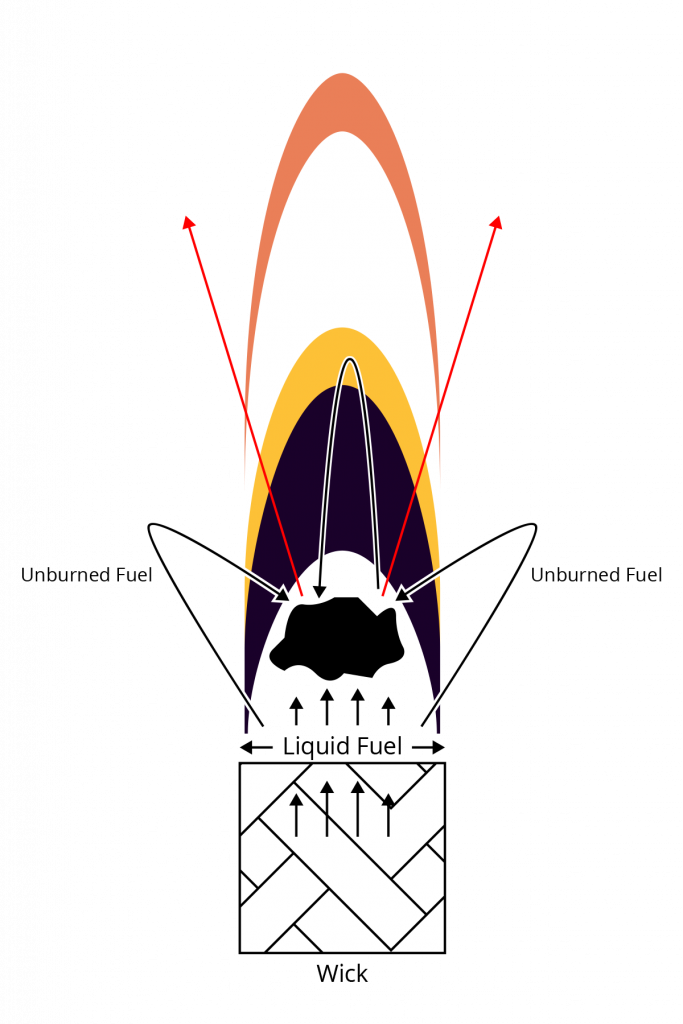
Fuel Reduction:
Mushrooming, carbon capping, or carbon deposits are the result of unburned fuel and soot accumulating on the end of the wick.
Ideal Complete Combustion:
All combustion takes place on the outside edge of the flame where oxygen and heat are at their maximum.